Evaluation of Oil Palm Empty Fruit Bunch Compost Application on Samhong Mustard (Brassica juncea L.) Cultivation in Polybags
Main Article Content
Nur Rizha Adi Kumara
Ade Sumiahadi
Background: Samhong is a mustard variety that is becoming increasingly popular in Indonesia. To increase its production, appropriate cultivation technologies are necessary, such as enriching the growing medium with organic matter. One organic material that can be utilized is compost made from oil palm empty fruit bunches (OPEFB). OPEFB is the solid waste remaining after oil has been extracted from the flesh (mesocarp) and kernel (endocarp) of fresh oil palm fruits.
Aims & Methods: This study aimed to evaluate the effects of different OPEFB compost dosages on the growth and yield of samhong mustard plants. The research was conducted from March to May 2023 at the Experimental Field of the Faculty of Agriculture, Universitas Muhammadiyah Jakarta. The study utilized a Randomized Complete Block Design (RCBD) with five treatment levels, consisting of a control group using inorganic NPK fertilizer and four different doses of OPEFB compost (25, 50, 75, and 100 g/plant).
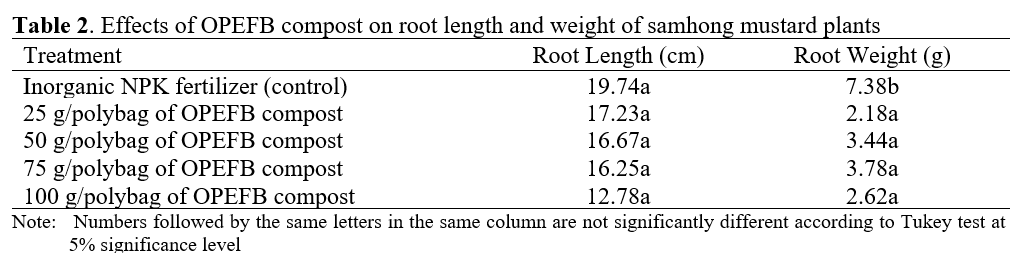
Result: The results of this study indicate that, in general, all OPEFB compost applications resulted in lower growth and yield compared to the NPK control. However, a positive trend was observed where higher compost doses led to improved plant growth. Furthermore, correlation analysis revealed a strong to very strong positive correlation between OPEFB compost dose and the growth of above-ground parts and yield of the plants. This study indicated that OPEFB compost has potential to be used as organic fertilizer with higher doses.
Andiyarto, H. T. C., & Purnomo, M. (2012). The effectiveness of vetiver grass (Vetiveria zizanioides) in controlling surface landslides on roadside slopes based on root growth response. Journal of Civil Engineering and Planning, 14(2), 151–164.
Ansyahri, A. A. (2021). The effect of vermicompost and NPK Mutiara 16:16:16 fertilizer on the growth and yield of pagoda mustard (Brassica norinosa). Undergraduate Thesis, Universitas Islam Riau, Pekanbaru.
Central Bureau of Statistics. (2020). Harvested area of vegetables by district/municipality and plant type in West Java Province. Jakarta: BPS-Statistics Indonesia.
Bell, C., & Egon, A. (2024). Plant root architecture and nutrient acquisition. EasyChair Preprint No. 14779. https://easychair.org/publications/preprint/H9QD
Cholisoh, K. N., Budiyanto, S., & Fuskhah, E. (2018). Growth and yield of mustard greens (Brassica juncea L.) as affected by rabbit urine fertilizer of different types and doses. Jurnal Agro Complex, 2(3), 275–280.
Firmansyah, I., Syakir, M., & Lukman, L. (2017). The effect of combined N, P, and K fertilizer doses on the growth and yield of eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). Journal Hortikultura, 27(1), 69–78.
Gunawan, M. R. (2024). The effect of oil palm empty fruit bunch (OPEFB) compost on the growth and yield of romaine lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). Undergraduate Thesis, Universitas Muhammadiyah Jakarta.
Habibah, P., Dwipa, I., & Satria, B. (2022). The effect of oil palm empty fruit bunch compost and watering interval on oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) seedling growth in the pre-nursery. Agrohita, 7(1), 202–209.
Hatta, M., & Permana, J. D. (2014). Utilization of oil palm empty fruit bunches as organic fertilizer in intercropping systems of oil palm and corn. Pengkajian dan Pengembangan Teknologi Pertanian, 17(1), 27–35.
Hendrika, G., Rahayu, A., & Mulyaningsih, Y. (2017). Growth of celery plants under various combinations of organic and synthetic fertilizers. Jurnal Agronida, 3(1), 1–9.
Herlina, N., Nelfia, & Puspita, P. (2015). Growth and yield of shallots (Allium ascalonicum L.) with application of formulated tricho-compost from oil palm empty fruit bunches and potassium fertilizer. Jurnal Photon, 6(1), 21–30.
Hidayat, M. (2019). Cultivation and Seed Production of Water Spinach. Jakarta: Ministry of Agriculture.
Ichriani, G. I., Nion, Y. A., Chotimah, H. E. N. C., & Jemi, R. (2016). Utilization of oil palm empty fruit bunch waste as biochar-microbes for improving soil nutrient availability. Journal of Degraded and Mining Lands Management, 3(2), 517–520.
Kamsurya, M. Y., & Botanri, S. (2022). The role of organic matter in maintaining and improving agricultural soil fertility. Jurnal Agrohut, 13(1), 25–34.
Leiwakabessy, F. M., & Sutandi, A. (2004). Fertilizers and Fertilization. Bogor: IPB (Bogor Agricultural University).
Lopez-Bucio, J., Cruz-Ramirez, A., & Herrera-Estrella, L. (2003). The role of nutrient availability in regulating root architecture. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 6, 280–287.
Marseta, A. (2021). The effect of growing media and NPK fertilizer doses on the growth and yield of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). Undergraduate Thesis, Universitas Teuku Umar Meulaboh, West Aceh.
Mas’ud, H. (2009). Hydroponic Systems Using Different Nutrients and Growing Media for Lettuce Growth and Yield. Palu: Research and Development Media.
Pahan, I. (2010). Complete Guide to Oil Palm Agribusiness Management from Upstream to Downstream. Jakarta: Penebar Swadaya.
Papageorgiou, S. N. (2022). On correlation coefficients and their interpretation. Journal of Orthodontics, 49(3), 359–361. https://doi.org/10.1177/14653125221076142
Perwitasari, B., Tripatmasari, M., & Wasonowati, C. (2012). The effect of growing media and nutrients on the growth and yield of pakchoi (Brassica juncea L.) in a hydroponic system. Agrovigor, 5(1), 14–25.
Polii, G. M. M. (2009). Production response of upland water spinach (Ipomoea reptans P.) to different times of chicken manure application. Journal of Soil and Environment, 1(7), 18–22.
Pratiwi, I. A., & Ardiansyah, H. D. (2019). A study of EFB (empty fruit bunch) for fuel in Indonesian biomass boilers. Ecology, Environment and Conservation, 25, 86–89.
Rahmah, A., Izzati, M., & Parman, S. (2014). The effect of liquid organic fertilizer made from Chinese cabbage (Brassica sinensis L.) waste on the growth of sweet corn (Zea mays L. var saccharata). Buletin Anatomi dan Fisiologi, 22(1), 65–71.
Rukmana, R. (2007). Cultivating Petsai and Pakcoy. Yogyakarta: Kanisius.
Safitri, A. A., Safwan, M., & Nurjani. (2013). The effect of oil palm empty fruit bunch bokashi on the growth and yield of corn in alluvial soil. Jurnal Sains Mahasiswa Pertanian Untan, 2(1), 1–9.
Santi, A., Rahayuni, T., & Santoso, E. (2018). The effect of oil palm compost on the growth and yield of radish in alluvial soil. Jurnal Untan Perkebunan dan Lahan Tropika, 8(1), 29–33.
Sarwono, E. (2008). The use of oil palm empty fruit bunches as a substitute fertilizer for oil palm plantations. Aplika: Jurnal Ilmu Pengetahuan dan Teknologi, 8(1), 19–23.
Satria, N., Wardati, & Khoiri, M. A. (2015). The effect of oil palm empty fruit bunch compost and NPK fertilizer on the growth of agarwood (Aquilaria malaccensis) seedlings. JOM Faperta, 2(1), 1–14.
Subagio, A. A., Mansur, I., & Sari, R. K. (2018). The use of oil palm empty fruit bunch compost to improve the growth of cajuput (Melaleuca cajuputi) on post-mining land. Jurnal Silvikultur Tropika, 9(3), 160–166.
Sulaeman, A., & Nurjasmani, R. (2017). Response of pakcoy to oil palm empty fruit bunches in a verticulture system. Jurnal Ilmiah Pertanian, 11(2), 714–717.
Sumartoyo. (2017). The effect of oil palm empty fruit bunch bokashi on the growth of sweet corn (Zea mays saccharata Stud) in PMK soil. PIPER, 13(24), 91–95.
Toiby, A. R., Rahmadani, E., & Oksana, O. (2015). Changes in the chemical properties of oil palm empty fruit bunches fermented with EM4 at various doses and fermentation durations. Jurnal Agroteknologi, 6(1), 1–8.
Nur Rizha Adi Kumara , Universitas Muhammadiyah Jakarta, Indonesia
Department of Agrotechnology, Faculty of Agriculture, Universitas Muhammadiyah Jakarta, Jakarta, Indonesia
Ade Sumiahadi , Uniersitas Muhammadiyah Jakarta, Indonesia
Department of Agrotechnology, Faculty of Agriculture, Universitas Muhammadiyah Jakarta, Jakarta, Indonesia